Packaging is essential for product presentation, protection, and branding, playing a vital role in the food, cosmetics, retail, and pharmaceutical industries. Product packaging serves multiple functions, including protecting products, enhancing brand identity, helping transport and storage, and conveying important information through labeling. Packaging has evolved from natural materials like leaves and clay to modern, eco-friendly designs, meeting the needs of businesses and consumers.
Packaging types are categorized by material (paper, plastic, glass, metal, wood), usage (custom, sustainable, flexible, retail, luxury, e-commerce, bulk), and function (primary, secondary, and tertiary). Packaging can be either custom or stock, depending on the specific needs of a brand, product, or business. Custom packaging is designed specifically for a product or brand, allowing for unique sizes, shapes, materials, and branding elements like logos, colors, and custom prints, while stock (pre-made) packaging offers a practical solution for general use at lower costs.
The packaging development process includes material selection, design refinement, durability testing, and supplier collaboration to ensure functionality and cost efficiency. Ordering custom packaging requires understanding your product’s needs, setting a budget, choosing suitable materials, designing the packaging, and selecting a reliable supplier.
- What is Packaging?
- What are the Types of Packaging?
- What is Custom Packaging?
- What is the Process of Packaging Development?
- How Can Packaging Improve the Marketing of a Product?
- Why is Packaging Design Important for Products?
- What is the Role of a Packaging Designer in Packaging?
- How does the Packaging Engineer Create Structural Packaging?
- Which Packaging Companies Provide Packaging for Products?
- How to Order Custom Packaging for Your Products?
- 1. Understand Your Packaging Needs
- 2. Estimate Your Packaging Budget
- 3. Select the Type of Packaging
- 4. Measure Box Dimensions for Product Packaging
- 5. Choose the Right Material for Your Product Packaging
- 6. Look for Sustainable Packaging Materials
- 7. Select the Box Style for Your Product Packaging
- 8. Create the Design of the Packaging
- 9. Choose the Appropriate Printing Option for Your Product Packaging
- 10. Select the Add-ons and Finishes
- 11. Find a Trusted Packaging Supplier
What is Packaging?
Packaging is the science, art, and technology of containing, protecting, and presenting items for marketing, storage, shipping, and use. Packaging is made of various materials such as paper, cardboard, plastic, glass, metal, or biodegradable substances, chosen based on the product’s specific requirements. Packaging is widely used across industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, electronics, and retail to enhance brand identity, protect products, preserve them, facilitate transportation and storage, and communicate essential information through labeling.
What is the History of Packaging?
The history of packaging mirrors the progression of human civilization, from using simple natural materials like leaves, animal skins, and gourds in ancient societies to the development of clay pots, woven baskets, and glassmaking techniques in subsequent eras. By the Middle Ages, advancements such as wooden barrels, parchment, and crates facilitated trade and storage, while the Industrial Revolution introduced transformative innovations like tin cans, paperboard, and corrugated cardboard, driven by mechanization and the need for mass production. The 20th century ushered in plastics, vacuum-sealing, and recyclable materials, revolutionizing packaging while addressing the growing demands of industrialization and environmental concerns.
Today, packaging integrates advanced materials, smart technologies, and sustainable solutions, with a focus on balancing functionality, consumer appeal, and ecological responsibility. Looking ahead, nanotechnology, IoT-enabled smart packaging, and circular economy principles are expected to shape the future, underscoring packaging’s role as a vital interface between products, consumers, and the environment.
What is the Purpose of Packaging?
Packaging serves multiple purposes, including marketing, branding, protecting, containing, preserving, transporting, and communicating, all while playing a vital role in the product’s usability and market appeal.
- Branding: Packaging establishes and communicates the product’s identity through the use of logos, colors, and designs. It also promotes brand recognition and loyalty by creating a distinct and memorable presence for consumers.
- Marketing: Packaging is used to attract buyers with visually appealing designs, effective messaging, and unique features. It influences purchase decisions and helps products stand out from competitors in a crowded market.
- Protection: Packaging protects the product from damage, contamination, and external factors like moisture, light, and temperature changes during storage, transportation, and handling.
- Containment: Packaging is used to hold the product, especially liquids, powders, and small items, for safe storage and shipping.
- Preservation: Packaging keeps the product fresh, safe, and intact throughout its shelf life by preventing spoilage or degradation.
- Shipping: Packaging ensures the safe and efficient transportation of products by protecting them from damage and keeping them organized for smooth handling during transit.
- Information Transmission: Packaging provides essential details like ingredients, usage instructions, safety warnings, expiration dates, and recycling guidelines, helping consumers make informed decisions.
- Convenience: Packaging simplifies handling, transport, and storage for both businesses and customers, making the product easy to use.
Packaging promotes, protects, preserves, transports, and informs, while enhancing usability and supporting sustainability, making it essential for both businesses and consumers.
What is Labeling in Packaging?
Labeling in packaging involves providing printed or graphic information on a container or article to communicate essential details about the product. Package labeling serves multiple purposes, including identifying the product, informing customers, and ensuring compliance with legal requirements. Package labels include details such as the product name, brand, ingredients, usage instructions, safety warnings, and expiration dates. These labels also feature barcodes, lot numbers, and recycling or handling symbols. Clear and accurate package labeling helps consumers make informed decisions, builds trust, and reinforces the brand’s identity. Labels play a vital role in packaging by enhancing functionality and appeal.

What are the Types of Packaging?
Packaging types are divided into three categories based on material, usage, and function. The materials include paper, plastic, glass, metal, and wood. Paper-based packaging, such as cardboard, paperboard, kraft paper, card stock, and corrugated fiberboard, is widely used in food, retail, and e-commerce industries. Packaging made from paper-based materials is eco-friendly, recyclable, and easily customizable for branding. Plastic is lightweight and versatile, often used for bottles and containers. Glass provides a premium look to the packaging, making it ideal for beverages and perfumes. Metal provides durability and protection, and it is commonly used in cans and tins. Wood is used mainly for crates and pallets in shipping.
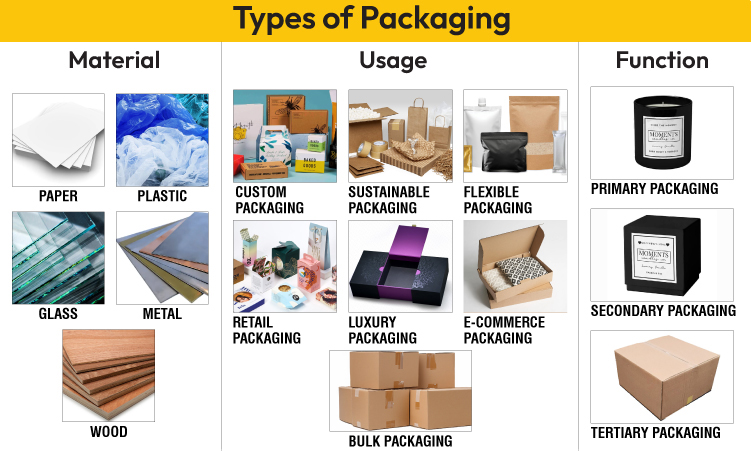
Packaging types based on usage include custom packaging, sustainable packaging, flexible packaging, retail packaging, luxury packaging, e-commerce packaging, bulk packaging, and product packaging. Custom packaging is made to fit a specific brand or product. Sustainable packaging incorporates eco-friendly materials such as recycled or biodegradable components. Flexible packaging is lightweight and easy to shape, often used for food. Retail packaging is designed to look attractive in stores, while luxury packaging uses high-quality materials for a premium feel. E-commerce packaging ensures product protection during shipping and enhances the unboxing experience. Bulk packaging is used to transport large quantities of goods safely. Product packaging refers to the immediate container or wrapping used to enclose a product, ensuring its safety, usability, and shelf appeal across various industries.
Packaging can be categorized into three types based on function, such as primary, secondary, and tertiary packaging.
What are Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Packaging?
Primary, secondary, and tertiary packaging are three layers of packaging based on their function to contain, protect, store, display, and transport products.

- Primary Packaging: Primary packaging directly holds and protects the product, ensuring safety and usability. Examples of primary packaging include bottles, cans, jars, pouches, tubes, wrappers, and blister packs.
- Secondary Packaging: Secondary packaging is used to group primary packages to facilitate handling, storage, distribution, or display. Secondary packaging includes cardboard boxes, shrink wrap, and mailing bags.
- Tertiary Packaging: Tertiary packaging is used for bulk handling, warehouse storage, and shipping to ensure safe and efficient transportation. Examples of tertiary packaging include pallets, stretch wraps, and shipping containers.
What is Custom Packaging?
Custom packaging is a type of packaging that is produced in the desired design, shape, material, and style to safely pack, store, and ship products like food, cosmetics, and candles while promoting the brand.
What is the Difference Between Custom Packaging and Stock (Pre-made) Packaging?
The main differences between custom and stock packaging lie in their level of personalization, cost, and purpose. Stock packaging is pre-made, generic packaging that offers standard sizes, limited customization, lower costs, and quick availability, making it ideal for basic needs and quick shipping. Custom packaging is designed specifically for a product, offering custom designs, styles, materials, sizes, and branding elements like logos and colors, creating a more premium and memorable customer experience. Stock packaging is ideal for startups, test marketing, or general shipping, while custom packaging is preferable for luxury goods, unique items, or businesses prioritizing branding and customer impressions.

What is the Process of Packaging Development?
The packaging development process involves a structured approach beginning with requirement analysis, where product specifications like dimensions, weight, and regulatory compliance are identified. Next, a concept design phase incorporates structural, material, and visual elements to create an initial model. This is followed by material selection, evaluating options such as paperboard or biodegradable polymers for cost-effectiveness and sustainability. The prototyping stage then develops physical or digital models to test practicality and performance. Rigorous testing and validation ensure durability and functionality through methods like drop tests and environmental simulations. A detailed cost analysis optimizes expenses by assessing material efficiency and production workflows. Finally, the design is finalized and moved to mass production, ensuring adherence to quality standards through automated processes and detailed specifications.
The seven key steps in the packaging development process are given below:
- Requirement Analysis
- Concept Design
- Material Selection
- Prototyping
- Testing and Validation
- Cost Analysis and Optimization
- Finalization and Production
How Much Does Packaging Cost?
Packaging cost commonly ranges from about $0.50 per unit for a small, simple one-piece box to about $1.00 per unit for a larger, multi-piece paperboard package with complex folding. The components of packaging cost include material expenses, design intricacies, printing and finishes, tooling fees, labor costs, and freight and delivery charges, all of which collectively influence the overall expenditure.
How Can Packaging Improve the Marketing of a Product?
Packaging improves product marketing by creating strong first impressions, attracting customer attention, and differentiating products from competitors. Custom packaging communicates a brand’s identity through consistent use of logos, colors, and typography, while also highlighting product benefits and features. Functional packaging enhances customer experiences with practical features such as resealable, easy-to-open designs and convenient elements like easy-pour spouts or handles, which add value and differentiate brands. According to a European Journal of Marketing study from the Marketing and Innovation Department, functional packaging increases purchase intentions by enhancing product meaningfulness and creating a strong first impression, especially for low-complex products. Eco-friendly packaging, made from recyclable or biodegradable materials, reduces waste and appeals to environmentally conscious consumers. Interactive packaging engages customers with promotional elements like QR codes or special offers. Effective product packaging boosts sales, strengthens brand loyalty, and increases brand awareness by incorporating functional features, sustainable materials, and engaging design elements.
How Can Packaging Increase Brand Awareness?
Packaging increases brand awareness by making products easily recognizable through consistent use of logos, colors, designs, typography, and images. According to research from the Design Department at Southern New Hampshire University, Color enhances brand recognition by up to 80%, highlighting how a strong visual identity improves brand recall. Eye-catching packaging captures attention, reflects brand values, builds trust, and helps customers connect emotionally with the brand. Custom packaging serves as a visual representation of the brand, maintains a consistent look across products, makes it easier for consumers to recognize and remember the brand, encourages loyalty, and stands out in stores. According to the Pennsylvania State University’s research from the Department of Consumer Psychology,brand image conveyed through packaging plays a crucial role in shaping consumer perception of product quality and influencing purchasing decisions.
Why is Packaging Design Important for Products?
Packaging design is crucial for products as it effectively communicates their benefits, attracts buyers with eye-catching visuals, and enhances functional usability. According to a study conducted by the Paper and Packaging Board and IPSOS, 72% of American consumers state that the design of a product’s packaging often influences their purchase decisions. Well-designed packaging improves the overall consumer experience and strengthens brand identity.
What is the Role of a Packaging Designer in Packaging?
Packaging designers are tasked with conceptualizing and executing designs that balance functionality, aesthetics, and brand alignment. Their responsibilities include determining the shape, size, and material of packaging, as well as incorporating graphics, typography, and finishes to create a cohesive design. Packaging designers collaborate with clients to understand business objectives, ensuring the final product meets both practical and marketing requirements. These designers also oversee the production process, approving print proofs to maintain color accuracy and consistency.
How does the Packaging Engineer Create Structural Packaging?
Packaging engineer creates structural packaging by designing and testing materials and structures to ensure product safety, usability, and cost-efficiency. Packaging engineers analyze the product’s characteristics, transportation requirements, and environmental impact to design a package structure using appropriate materials like corrugated cardboard and strategically incorporate features like folds, creases, and reinforcements.
Which Packaging Companies Provide Packaging for Products?
Packaging companies that primarily offer stock or pre-made packaging for products are listed below.

- Uline
- Amcor
- WestRock
- Ball Corporation
- Berry Global
- Sealed Air
- Crown Holdings
- Sonoco
These packaging companies provide standard packaging such as boxes, bags, wraps, and containers that are pre-made and designed to meet general requirements. However, they do not offer customization for specific branding or design needs. In contrast, Packhit specializes in custom packaging, enabling businesses to create product packaging tailored to their brand, design, material, and style requirements.
How to Order Custom Packaging for Your Products?
To order custom packaging for your products, you need to assess your product’s dimensions and requirements, set a budget by calculating material and design costs, choose suitable packaging and materials, determine box dimensions and style, design the packaging, select printing and finishing options, and partner with a reliable packaging supplier.
Follow the steps given below to order custom packaging for your products.
- Understand Your Packaging Needs
- Estimate Your Packaging Budget
- Select the Type of Packaging
- Measure Box Dimensions for Product Packaging
- Choose the Right Material for Your Product Packaging
- Look for Sustainable Packaging Materials
- Select the Box Style for Your Product Packaging
- Create the Design of the Packaging
- Choose the Appropriate Printing Option for Your Product Packaging
- Select the Add-ons and Finishes
- Find a Trusted Packaging Supplier
1. Understand Your Packaging Needs
Begin by assessing your product’s dimensions, weight, and specific requirements for storage, marketing, shipping, and protection. Identify your branding goals and the functional features needed to ensure that your packaging aligns with your target audience’s expectations.
2. Estimate Your Packaging Budget
Calculate your packaging costs by factoring in material type, design complexity, order quantity, and printing options. Determine the cost per unit to ensure it stays within your budget constraints.
3. Select the Type of Packaging
Choose the appropriate packaging type, such as boxes, pouches, tubes, or wrappers, based on your product’s size and intended use. For example, fragile products may require durable materials for protection, while retail products benefit from visually appealing options like display boxes.
4. Measure Box Dimensions for Product Packaging
To accurately measure box dimensions for product packaging, measure the length (L), width (W), and height (H) of the box using a ruler or measuring tape, considering both internal and external dimensions. Record the measurements in L × W × H format in inches or centimeters, double-check for accuracy, and account for additional packaging needs such as protective materials, flaps, and weight restrictions. Accurate box measurements help optimize packaging fit, protection, and shipping efficiency.
5. Choose the Right Material for Your Product Packaging
Select appropriate packaging materials based on durability, cost, and environmental impact. Common materials for custom packaging include cardboard, paperboard, corrugated cardboard, kraft paper, card stock, and rigid.
6. Look for Sustainable Packaging Materials
Opt for eco-friendly materials such as cardboard, recycled paper, or reusable packaging for your product packaging to support sustainability goals and attract environmentally conscious consumers.
7. Select the Box Style for Your Product Packaging
Select a box style that best suits your product, such as mailer boxes, display boxes, or tuck end boxes. Ensure the chosen box style aligns with both functionality and branding to enhance product presentation and protection.
8. Create the Design of the Packaging
Create an eye-catching packaging design incorporating brand elements such as logos, colors, and graphics to enhance customer engagement. Work with a professional designer or submit pre-made artwork to your packaging supplier to create a custom design that reflects your brand identity.
9. Choose the Appropriate Printing Option for Your Product Packaging
Selecting the right printing method for your packaging depends on your budget, material, design, and production requirements. Digital printing is great for small batches and fast production, while offset printing provides high-quality images for large orders. Flexographic printing is best for high-speed printing on flexible materials, and screen printing works well for bold designs on rigid surfaces. Gravure printing is ideal for large-scale, high-quality prints. Choosing the right printing method ensures your packaging is visually appealing and functional.
10. Select the Add-ons and Finishes
Select finishes like coatings, laminations, foil stamping, embossing, debossing, and spot UV coating to enhance the visual appeal of the product packaging. Coatings such as matte, gloss, satin, or soft-touch not only improve the tactile feel but also provide a protective layer that enhances durability and resists scuffs or scratches.
Incorporate additional features such as foam inserts, cardboard dividers, die-cut handles, magnetic closures, ribbon closures, window cutouts, custom inserts, QR codes, NFC tags, security seals, and tamper-proof features to enhance functionality, security, and user experience.
11. Find a Trusted Packaging Supplier
Partner with a reliable packaging supplier to produce high-quality custom packaging in the required quantities within your timeline and budget. Verify their experience and customer reviews to ensure reliability.

