To make custom packaging, begin by identifying your product’s size, weight, and branding needs. Based on these factors, choose the appropriate packaging type, such as boxes, pouches, tubes, or wraps, that best suits both functionality and product presentation. Next, select a suitable box style, such as a mailer, tuck-end, two-piece, or magnetic closure, to enhance the unboxing experience. Once the style is determined, opt for materials like cardboard, corrugated fiberboard, or rigid, considering both durability and cost-effectiveness. After selecting the material, measure accurate dimensions to ensure a snug fit for your product. With these specifications in place, create a dieline template and design the custom packaging with brand-aligned colors, typography, and logos to establish a strong visual identity.
After finalizing the design, choose a printing method such as digital, offset, or screen printing and consider adding premium finishes like embossing or foil stamping to elevate the overall look of the packaging. Before proceeding with mass production, create a prototype to test the packaging’s functionality, durability, and aesthetic appeal. Lastly, collaborate with a reliable packaging supplier to ensure high-quality manufacturing, cost efficiency, and timely delivery of your custom packaging.
The ten-step process of creating custom packaging is shown in the diagram below.

- 1. Understand your Packaging Needs
- 2. Select the Type of Packaging
- 3. Choose the Style of Packaging
- 4. Choose the Right Material for your Packaging
- 5. Measure the Size of your Packaging
- 6. Create a Dieline for the Packaging
- 7. Create the Design of the Packaging
- 8. Print the Artwork and Finishes on the Packaging
- 9. Finalize the Prototype and Testing
- 10. Find the Trusted Supplier for Production
- How to Choose the Right Custom Packaging for your Product?
1. Understand your Packaging Needs

Understanding your packaging needs before selecting the type of packaging is essential to ensure that the chosen design, materials, and style effectively protect the product, meet regulatory requirements, align with branding goals, and stay within budget constraints. After defining your packaging needs, the next step is choosing the right type of packaging.
2. Select the Type of Packaging

Selecting the right type of packaging before choosing a packaging style is essential because it helps determine the best style that fits the product’s protection, functionality, and presentation needs. Once the appropriate packaging type is determined, proceed with selecting a suitable packaging style.
3. Choose the Style of Packaging

Choosing the right packaging style first is essential because it determines the structural design, functionality, and branding requirements, allowing you to select a material that provides the necessary durability, protection, and visual appeal for custom packaging. When the style is chosen, the next step is to select the most suitable packaging material.
4. Choose the Right Material for your Packaging

Selecting the right material before measuring your packaging size is essential, as different materials vary in thickness, flexibility, and structural integrity, directly affecting the internal and external dimensions required for a secure and precise fit. As soon as you choose the packaging material, you must ensure accurate box measurements to achieve a snug fit for your product.
5. Measure the Size of your Packaging

Measuring the size of your packaging before creating a dieline is essential, as it ensures accurate dimensions for a precise layout, proper fold and cut lines, and adequate bleed areas, preventing misalignment and optimizing material usage for cost-effective packaging.
6. Create a Dieline for the Packaging
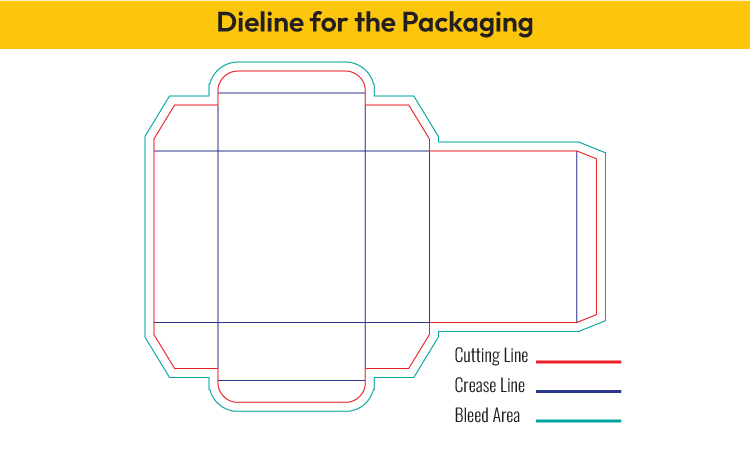
Creating a dieline before designing the packaging is essential, as it provides a precise template that ensures accurate placement of design elements, prevents misalignment, accommodates necessary folds and cuts, and helps visualize the final packaging’s appearance and functionality, leading to a seamless and professional design. The dieline then serves as the foundation for a visually appealing and functional packaging design.
7. Create the Design of the Packaging

Creating the design of the packaging before printing the logo and adding finishes is essential as it provides a structured layout that ensures precise logo placement, proper alignment of design elements, and optimal positioning for finishes, resulting in a polished and professional final product. Once the design is complete, the next step is printing it on the packaging.
8. Print the Artwork and Finishes on the Packaging


Printing the artwork and finishes on the packaging before finalizing the prototype and testing is essential as it allows for a realistic evaluation of the final product’s appearance, durability, and customer perception, ensuring necessary refinements before mass production.
9. Finalize the Prototype and Testing


10. Find the Trusted Supplier for Production
How to Choose the Right Custom Packaging for your Product?
To choose the right packaging for your product, consider factors such as product type, branding requirements, budget, transportation, materials, size, functionality, and environmental impact. Ensure the packaging aligns with your brand message while being cost-effective, durable, and practical for transport. Choose materials that balance protection and sustainability, optimize size to reduce costs, and design the packaging for both visual attraction and ease of use.
What Type of Custom Packaging is used for a Product?
There are different types of custom packaging used for the product, such as boxes, bags, pouches, tubes, trays, sleeves, and wraps, each serving specific purposes based on product requirements. Boxes are sturdy, stackable, and customizable, used to protect and brand products like toys, cosmetics, medicines, appliances, food, and beverages. Bags are flexible, lightweight, and portable, used to conveniently carry and package products such as groceries, apparel, and takeout food. Pouches are resealable, airtight, and space-efficient, used to preserve freshness and extend the shelf life of items like snacks, coffee, pet food, and supplements. Tubes are squeezable, tamper-evident, and easy to dispense, used to store and apply liquid or semi-liquid products like creams, lotions, ointments, gels, toothpaste, sauces, and condiments. Trays are rigid, stackable, and protective, used to support and display perishable or fragile products, and are used for fresh produce, meat, seafood, and bakery items. Sleeves are minimalist, customizable, and cost-effective, used to enhance branding without full coverage for products like soap bars, chocolates, and beverage bottles. Wraps are flexible, protective, and lightweight, used to maintain freshness and prevent contamination, commonly used for candy bars, sandwiches, and baked goods.
What are the Key Design Elements to Consider for the Custom Packaging of a Product?
The key design elements to consider for custom packaging of a product include visuals such as color schemes that evoke specific emotions, a distinctive logo that reinforces brand identity, cohesive graphics to enhance visual appeal, typography that matches the brand’s style while remaining easy to read, and thoughtfully designed artwork to differentiate the product on the shelf.
How can Custom Packaging Impact Brand Identity?
Custom packaging can impact brand identity by enhancing brand recognition through consistent use of logos, colors, and typography, making it easier for customers to identify and remember a brand. According to research conducted by the International Journal of Scientific Research in Engineering and Management (IJSREM), 46.7% of respondents agreed that packaging color impacts consumer buying behavior, while 18.7% strongly agreed. This indicates that custom-printed packaging creates a strong first impression by capturing attention and conveying quality through eye-catching design, premium materials, personalization, and functionality, ultimately encouraging customers to choose the product. Custom packaging also differentiates a brand from competitors through unique and innovative designs, making the product more memorable.
Which Printing Technique is best for Logo Printing on custom Packaging?
Struggling to find the best printing method while creating custom packaging for your brand?
Get expert guidance and high-quality custom packaging from Packhit today!

