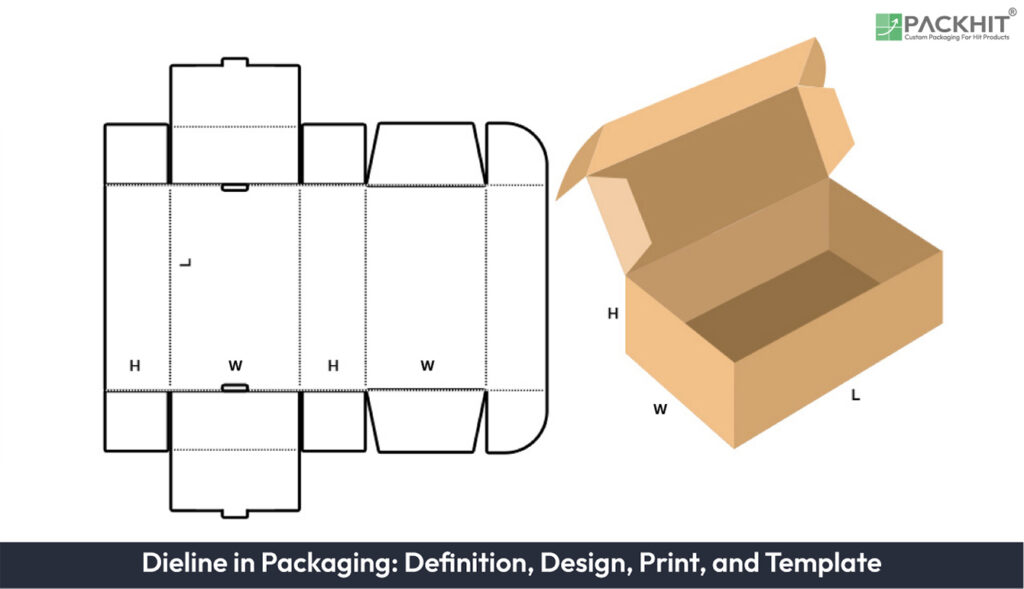
A dieline is a detailed template used in packaging design that includes cut lines, fold lines, bleed areas, and safe zones to ensure accurate printing and cutting. It includes elements like cut lines, fold lines, bleed areas, and safe zones to guide production. Dielines are created using tools like Adobe Illustrator or ArtiosCAD through steps such as defining dimensions, outlining structural elements, layer separation, and prototype testing. They play a vital role in ensuring dimensional accuracy, brand consistency, and sustainability by optimizing material use. Commonly applied in food, electronics, pharmaceuticals, and beverage packaging, dielines help align graphics with structure for error-free printing. Box dieline templates further streamline design by providing ready-made structures. While common errors include misalignment and wrong dimensions, they can be avoided through expert collaboration, proper software use, and prototype testing.
- What is a Dieline in Packaging?
- What are the Different Types of Lines and Areas used in a Dieline?
- What is the Main Purpose of a Dieline?
- How are Dielines Created in Packaging?
- 1. Define Dimensions
- 2. Outline Structural Elements
- 3. Layer Separation
- 4. Test Feasibility
- Tools Used in Dieline Creation:
- What is the Role of Dielines in Packaging Design?
- What are the Major Applications of Dielines?
- What are the Benefits of Using Dielines?
- What is the Role of Dielines in the Printing of Packaging?
- What are Box Dieline Templates in Packaging?
- What are the Common Errors in Dieline Design?
What is a Dieline in Packaging?
A dieline is a 2D template that outlines the layout, dimensions, and structural elements of packaging designs. It ensures precision in cutting, folding, and assembling packaging materials, making it an essential tool for manufacturers and designers. Dielines apply to various packaging types, including boxes, labels, bottles, and brochures.
What are the Different Types of Lines and Areas used in a Dieline?
The various types of lines and areas used in a dieline are mentioned below:
- Cut Lines: Indicate where the packaging material will be cut, ensuring precise edges.
- Fold Lines: Define where the material will be folded, ensuring accurate assembly.
- Bleed Areas: Provide extra space to extend design elements beyond cut lines, preventing errors during cutting.
- Safe Zones: Ensure critical design elements like text and logos remain within non-cuttable areas.
What is the Main Purpose of a Dieline?
The primary purpose of a dieline is to ensure that packaging is functional, visually appealing, and meets production specifications. It acts as a guide for designers, printers, and manufacturers, reducing errors, optimizing material usage, and enhancing branding consistency.
How are Dielines Created in Packaging?
Dielines are typically created by graphic designers or packaging engineers using specialized software such as Adobe Illustrator or ArtiosCAD. The process involves defining cut lines, fold lines, bleed areas, and safe zones based on product dimensions and design requirements.
The main steps in dieline creation are listed below:
1. Define Dimensions
Measure product length, width, and height in inches or millimeters. Record irregular shapes by measuring the largest, smallest, and average cross sections. Add clearance for inserts and padding, for example, 1/16 inch per side for a snug fit. Note product weight and any protrusions such as handles or connectors. Place these numbers on a one-page spec sheet for the dieline file.
2. Outline Structural Elements
Map cut lines, fold lines, glue flaps, perforations, and ventilation holes directly onto the template. Set bleed to 0.125 inches or 3 millimeters beyond cut lines. Set a safe zone of at least 0.125 inches from cut lines for logos and text. Mark crease lines as dashed and cut lines as solid to avoid confusion during production. Indicate glue areas and tab positions, and add a 2 to 5 millimeter allowance for material thickness when designing locking or interlocking tabs.
3. Layer Separation
Create distinct layers for dieline, artwork, cutting, and printing marks. Name layers using clear labels such as DIELINE, ARTWORK, CUTTER, and BLEED. Lock the dieline layer and set it to a single spot color that the printer recognizes. Keep photographic images at 300 dpi and place vector art on its own layer. Save working files in AI and export final files as PDF/X for prepress handoff.
4. Test Feasibility
Build at least one digital mockup and one physical prototype to test the dieline. Cut and fold a paper or corrugated sample to check fit, closure, and stacking. Measure critical gaps and tolerate 1/16 inch for folding and glue variance. Run a color proof to confirm registration and bleed. If the prototype fails any check, revise the dieline and repeat the prototype step until dimensions and assembly pass.
Tools Used in Dieline Creation:
- Adobe Illustrator: Popular software for creating precise dieline templates.
- ArtiosCAD: Specialized software for structural packaging design.
- Dieline Generators: Online tools that allow customization of dieline templates.
What is the Role of Dielines in Packaging Design?
Dielines play a pivotal role in packaging design by providing a structured framework for creating custom packaging. They ensure dimensional accuracy, facilitate branding alignment, and promote sustainability through material efficiency.
Dimensional Accuracy
Dielines ensure packaging fits product dimensions accurately, preventing issues like oversized or undersized packaging. This precision is critical for industries such as food, electronics, and pharmaceuticals.
Branding Alignment
By collaborating with designers, dielines ensure that packaging reflects brand values and maintains visual consistency. Defined areas for logos, text, and images enhance aesthetic appeal and reinforce brand identity.
Sustainability Contribution
Dielines optimize material utilization, minimize waste, and endorse eco-friendly practices. This makes them a valuable tool for manufacturers aiming to reduce their environmental footprint.
What are the Major Applications of Dielines?
Dielines have widespread applications in packaging design, serving as essential templates for creating packaging that is both functional and visually aligned with branding objectives. They are used across various industries to design packaging for products such as food, beverages, electronics, and pharmaceuticals.
Food Packaging
Food packaging ensures compliance with safety and hygiene standards and provides an accurate fit for products such as snacks, frozen foods, and baked goods. Dielines for food packaging define barrier layers, resealable zippers, and portioning panels. Materials commonly used include coated paper foil laminates and heat-seal films. Dielines mark label areas for nutrition facts, ingredient lists, and lot codes, indicating tamper evidence and ventilation where required for refrigerated items.
Electronics Packaging
Electronics packaging provides structural integrity, cushioning, and protection for fragile or high-value items like mobile phones and accessories.
Dielines for electronics include die cut foam inserts, ESD safe liners, and multi-stage folds to distribute shock. Typical dieline notes specify 2 to 5 millimeter fit tolerance for connectors and cables, and call out barcode panels and assembly tabs for efficient packing. Corrugated grades and double-wall options are often indicated to meet shipping and stacking requirements.
Pharmaceutical Packaging
Pharmaceutical packaging guarantees dimensional precision and adherence to regulatory requirements for medicines, supplements, and medical devices. Dielines for pharmaceuticals specify child-resistant tamper-evident seals, and clear areas for lot numbers and expiration dates. Substrate choices include FDA-compliant papers and moisture barrier films.
Beverage Packaging
Beverage packaging facilitates the design of customized bottle carriers, cans, and cartons, ensuring durability and brand appeal.
Dielines control handle placement, stacking strength, and ventilation for chilled products. They list flute-type corrugation grades, glue patterns, and reinforcement points to meet load specifications. Common examples include six-pack carriers, sleeve wraps, and multi-can shippers that integrate die-cut grips and proof points for retail display.
What are the Benefits of Using Dielines?
The benefits of using dielines are detailed below:
Error Prevention
Error prevention reduces production mistakes by mapping every cut, fold, and glue area on the dieline. Designers separate structural lines from artwork and lock the dieline layer so printers cut and fold where intended. Preflight checks catch missing bleeds and incorrect color modes before plates reach the press. Physical prototypes expose fit and closure problems early. After the dieline passes a proof run, teams avoid misalignments such as artwork shifted across a panel and text truncated at a fold.
Material Efficiency
Material efficiency lowers waste and reduces packaging spend through smarter layout and structure choices. A tight dieline nests panels and optimizes the die layout to use the press sheet more completely. Designers specify the correct substrate and grain direction to reduce curling and scoring losses. Structural tweaks remove excess void and trim unnecessary flaps, so less substrate moves to landfill. Examples of savings include rotating panels to fit more shapes on a sheet and reducing unused liner areas on the web.
Enhanced Branding
Brand consistency keeps logos, text, and imagery intact across production and display. Dielines set safe zones and bleed areas so critical graphics never fall into a cut or fold. Clear registration marks and a dedicated artwork layer maintain alignment across print runs and press types. Color callouts and proofing notes preserve brand color and finish choices through the print process. Examples of practical alignment include placing a logo away from a scored edge and aligning a front panel artwork with a display window so the product presents the intended face on retail shelves.
What is the Role of Dielines in the Printing of Packaging?
Dielines are essential in packaging printing as they serve as a precise guide for aligning artwork with structural components. They define critical areas such as cut lines, fold lines, bleed areas, and safe zones, ensuring accurate placement of design elements like text and graphics. Proper dieline preparation minimizes errors during printing, enhances the visual appeal of the final product, and ensures consistency in packaging quality. This makes dielines indispensable for achieving professional and error-free packaging results.
What are Box Dieline Templates in Packaging?
Box dieline templates are pre-designed, customizable layouts that specify the structure, dimensions, and folding patterns for box packaging. These templates include key components such as cut lines, fold lines, bleed areas, and safe zones, ensuring precise alignment during production. Box dieline templates are commonly used for creating packaging for retail boxes, shipping cartons, and display boxes, and they help streamline the design process by providing a functional framework tailored to specific product dimensions and branding needs.
What are the Common Errors in Dieline Design?
Despite their benefits, dielines can be error-prone if not created accurately. Common errors include misaligned graphics, incorrect dimensions, and insufficient bleed areas, which can lead to costly production errors.
How to Avoid Mistakes while Creating a Dieline?
To avoid mistakes while creating a dieline, keep the following in mind:
- Collaborate with Experts: Work with professional designers and engineers to ensure accuracy.
- Test Prototypes: Create prototypes to identify and correct errors before production.
- Use Specialized Software: Leverage tools like Adobe Illustrator and ArtiosCAD for precision.
By understanding the dieline, its components, creation process, and applications, manufacturers can leverage dielines to produce high-quality, sustainable packaging that meets industry standards and enhances brand identity.