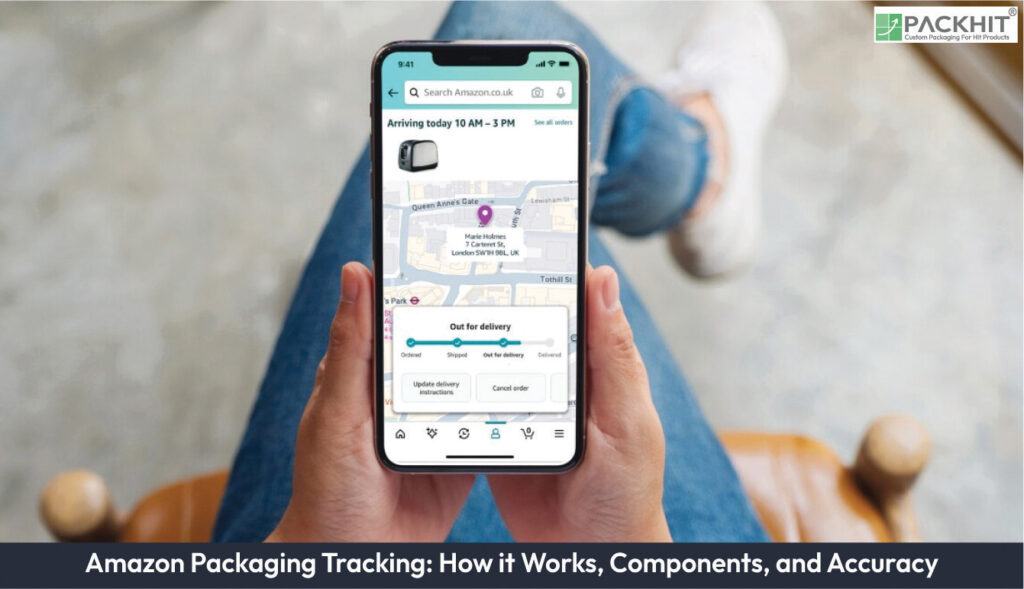
Amazon Packaging Tracking integrates advanced logistical frameworks to monitor, update, and notify stakeholders about shipments. It employs barcode scanning, real-time status updates, and automated notifications, enabling seamless tracking from origin to destination. Barcodes serve as unique identifiers, encoding essential details to ensure accurate data transmission at key checkpoints. The system’s three-stage workflow is creation, transit, and delivery, ensuring comprehensive visibility, while cloud-based infrastructure supports real-time updates. Status updates provide actionable insights, and automated notifications enable efficient communication. Manufacturers benefit from enhanced supply chain transparency, improved inventory management, and scalable operations. Despite limitations like barcode dependency and network-related delays, Amazon mitigates errors through redundancy checks, predictive algorithms, and routine audits. Manufacturers can optimize usage by ensuring proper barcode handling, leveraging notification customization, and integrating tracking data with inventory systems.
- How Does Amazon Packaging Tracking Work?
- What Are the Key Components of Amazon Packaging Tracking?
- How Does Amazon Ensure Accuracy in Packaging Tracking?
- Barcode Redundancy Checks
- Real-Time Data Validation
- Error Correction Algorithms
- Cloud-Based Infrastructure
- Routine Workflow Audits
- How Can Manufacturers Optimize Their Use of Amazon Packaging Tracking?
How Does Amazon Packaging Tracking Work?
Amazon Packaging Tracking operates through a multi-faceted system designed to ensure precise monitoring and seamless logistical management. This system integrates barcode technology, stage-based workflows, and real-time data processing to track packages effectively from creation to delivery.
Barcode Integration
Amazon tracks packaging through a barcode system, which assigns unique identifiers to every package. These barcodes encode essential details such as package ID, destination, and shipping method. Scanning devices capture this information at critical checkpoints, such as warehouses and transit hubs, ensuring data is transmitted to Amazon’s centralized system for real-time updates. This approach enables manufacturers and consumers to access accurate package location and progress details throughout the shipping process.
Workflow Stages
The tracking workflow consists of three stages: creation, transit, and delivery. In the creation stage, barcodes are generated and attached to packages, serving as the primary tracking mechanism. During transit, these barcodes are scanned at predefined checkpoints, prompting automated status updates. The final stage is delivery, marked by a confirmation scan, closing the tracking loop, and verifying receipt by the recipient. This structured workflow ensures detailed visibility and accountability at every step.
Real-Time Data Processing
Amazon employs cloud-based infrastructure to handle real-time data integration, allowing instantaneous updates from scanning devices to the centralized system. This enhances transparency by providing stakeholders with the most current information on package status. The system also enables proactive management by flagging anomalies such as delays or reroutes, ensuring timely resolution and maintaining high levels of customer satisfaction.
What Are the Key Components of Amazon Packaging Tracking?
The key components of Amazon packaging tracking are detailed below:
Barcode
Barcodes are the foundational element of Amazon Packaging Tracking. Each barcode encodes critical information, including the package ID, destination, and shipping method. Amazon employs 1D and 2D barcode formats, such as Code 128 and QR codes, to optimize data density and scanning efficiency. These barcodes are compatible with a wide range of scanning devices, ensuring interoperability across different logistical environments.
The barcode system is designed to minimize errors and maximize speed. High-resolution printing ensures legibility, while redundancy checks prevent data corruption during scanning. Amazon’s barcode infrastructure supports batch processing, enabling simultaneous tracking of multiple packages.
Status Update Protocols
Status updates are generated at predefined checkpoints throughout the shipping process. These updates include timestamps, location data, and event descriptions (e.g., “Package received at warehouse,” “Out for delivery”). Amazon’s tracking system categorizes status updates into actionable events, such as delays, reroutes, or successful deliveries, allowing manufacturers to respond proactively.
The frequency of status updates depends on the shipping method and route complexity. For example, expedited shipments may receive hourly updates, while standard deliveries might update less frequently. Amazon’s system also integrates predictive analytics to estimate delivery times based on historical data and current conditions.
Notification Architecture
Amazon Packaging Tracking employs an automated notification system to keep stakeholders informed. Notifications are triggered by specific events, such as package dispatch, transit milestones, or delivery confirmation. These alerts are delivered via multiple channels, including email, SMS, and app-based push notifications, ensuring accessibility for all users.
Manufacturers can customize notification preferences to align with their operational needs. For instance, high-priority shipments may require real-time alerts, while routine deliveries might only need end-of-day summaries. Amazon’s notification system also supports integration with third-party platforms, enabling seamless communication across diverse supply chain networks.
How Does Amazon Ensure Accuracy in Packaging Tracking?
There are multiple ways in which Amazon ensures accuracy in packaging tracking, such as barcode redundancy checks or real-time data validation, which are given below:
Barcode Redundancy Checks
Amazon Packaging Tracking employs barcode redundancy checks to minimize errors during scanning. These checks involve validating the encoded data multiple times across different devices and checkpoints. By ensuring that barcodes are accurately read and interpreted, Amazon prevents discrepancies in tracking information, maintaining the reliability of its system.
Real-Time Data Validation
The system incorporates real-time data validation mechanisms to verify the accuracy of information as it is transmitted. Each scanned update is cross-checked against pre-existing records in Amazon’s centralized database, ensuring that errors such as duplicate entries or conflicting statuses are promptly identified and rectified.
Error Correction Algorithms
Amazon utilizes advanced error correction algorithms to mitigate issues arising during data transmission or barcode scanning. These algorithms analyze discrepancies, apply corrective measures, and restore accurate tracking data, ensuring seamless updates for stakeholders.
Cloud-Based Infrastructure
The tracking system is built on a robust cloud-based infrastructure, offering high scalability and reliability. This infrastructure supports real-time data processing and storage, enabling instantaneous updates while reducing the risk of system downtime or data loss.
Routine Workflow Audits
Amazon conducts routine audits on its tracking workflows to identify bottlenecks and optimize system performance. These audits review checkpoint configurations, evaluate the efficiency of data transmission protocols, and ensure compliance with industry standards, further enhancing the precision of the tracking system.
How Can Manufacturers Optimize Their Use of Amazon Packaging Tracking?
Manufacturers can optimize their use of Amazon Packaging Tracking by implementing best practices. First, ensure that barcodes are printed and affixed correctly to prevent scanning errors. Second, leverage Amazon’s notification customization options to align tracking updates with operational priorities. Third, integrate tracking data with inventory management systems to enhance supply chain efficiency.
Additionally, manufacturers should train their staff to interpret tracking data and respond to status updates effectively. This training minimizes delays and ensures proactive decision-making. Finally, manufacturers can collaborate with Amazon to address specific logistical challenges, such as high-volume shipments or complex delivery routes. “`