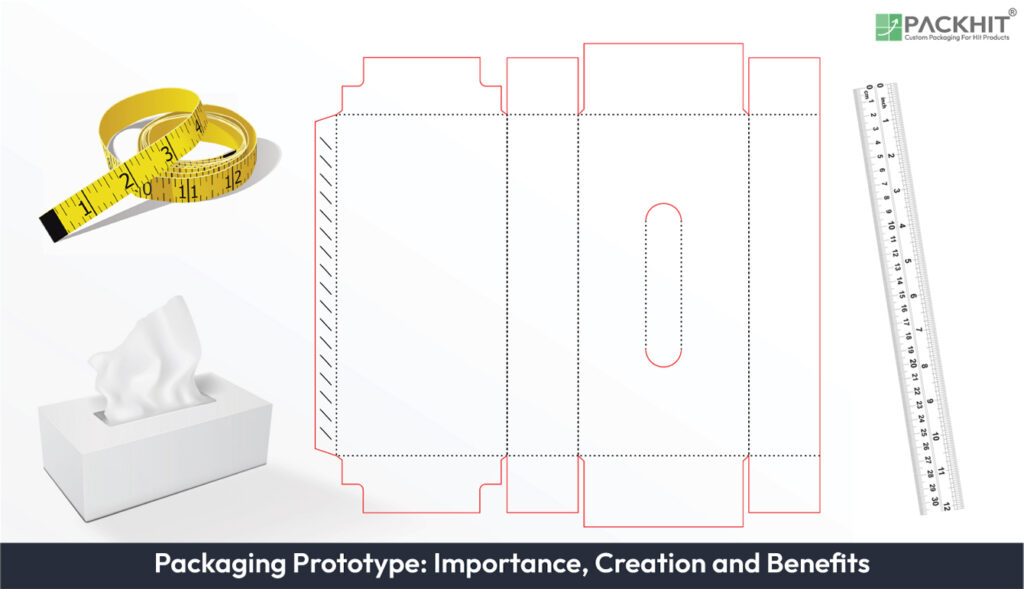
A packaging prototype is a pre-production model that replicates the final packaging’s materials, structure, and appearance to evaluate design, functionality, and usability before mass production. These prototypes, either physical, digital, or hybrid, simulate material properties, dimensions, branding elements, and functional features like closures for comprehensive testing. Their purpose varies by application: fragile items may require strength testing, while retail packaging emphasizes visual appeal, with digital tools enabling quick iterations and physical models providing tactile feedback.
Prototypes are crucial for identifying design flaws, improving cost efficiency, enhancing user experience, and ensuring compliance with regulations. The creation process includes conceptual design using CAD tools, material selection based on product needs, fabrication via methods like 3D printing or die-cutting, and iterative testing for refinement. They accelerate time-to-market, foster collaboration among stakeholders, boost competitiveness through optimized design, and support sustainability goals. Packaging prototypes find applications across industries from retail and logistics to marketing and compliance testing, making them essential in bridging concept and production.
- What is a Packaging Prototype?
- What are the Properties of Packaging Prototypes?
- How Do Packaging Prototypes Differ Based on Their Purpose?
- Why are Packaging Prototypes Important?
- How are Packaging Prototypes Created?
- What are the Benefits of Packaging Prototypes?
- 1. Accelerated Time-to-Market
- 2. Improved Stakeholder Collaboration
- 3. Competitive Advantage
- 4. Sustainability
- What are the Uses of Packaging Prototypes?
What is a Packaging Prototype?
A packaging prototype is a pre-production model of a product’s packaging, designed to simulate the final product in terms of dimensions, materials, and aesthetics. It can range from simple mockups to highly detailed, functional replicas. Prototypes are typically classified into three categories: physical prototypes, digital prototypes, and hybrid prototypes, each serving distinct purposes in the design and validation process.
What are the Properties of Packaging Prototypes?
Packaging prototypes are characterized by their ability to replicate materials, dimensions, visual elements, and functional features, enabling comprehensive evaluation of design, functionality, and usability before mass production.
- Material Simulation: Prototypes replicate the intended materials, such as cardboard, plastic, or glass, to test durability and compatibility.
- Structural Accuracy: They mimic the exact dimensions and structural features of the final packaging.
- Visual Representation: Prototypes include branding elements, colors, and finishes to evaluate aesthetic appeal.
- Functional Testing: Advanced prototypes may include closures, seals, or other functional components for usability testing.
How Do Packaging Prototypes Differ Based on Their Purpose?
Packaging prototypes vary based on their intended use. For instance, prototypes for fragile products may emphasize material strength, while those for retail displays prioritize visual impact. Additionally, digital prototypes, created using CAD software, allow for rapid iterations and virtual testing, whereas physical prototypes provide hands-on evaluation of tactile and structural properties.
Why are Packaging Prototypes Important?
Packaging prototypes play a pivotal role in bridging the gap between design concepts and production-ready solutions. Their importance lies in their ability to identify potential issues early, optimize design elements, and align packaging with brand identity and consumer expectations.
1. Risk Mitigation
Prototypes allow manufacturers to identify and address design flaws, material weaknesses, or functional inefficiencies before committing to large-scale production. This reduces the likelihood of costly recalls or product failures.
2. Cost Efficiency
By enabling iterative testing and refinement, prototypes minimize waste and ensure efficient use of resources. Digital prototypes, in particular, reduce material costs by allowing virtual testing.
3. Enhanced Consumer Experience
Prototypes help manufacturers evaluate the user experience, including ease of opening, resealing, and handling. This ensures the packaging meets consumer needs and enhances brand perception.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Prototypes are essential for verifying compliance with industry regulations, such as food safety standards, labeling requirements, and environmental guidelines.
How are Packaging Prototypes Created?
The creation of a packaging prototype involves a multi-step process that integrates design, material selection, and manufacturing techniques. Each step is tailored to meet the specific requirements of the product and its intended market.
1. Conceptual Design
The process begins with conceptualizing the packaging design, which includes determining dimensions, material types, and branding elements. Designers use software such as Adobe Illustrator or SolidWorks to create 2D and 3D renderings.
2. Material Selection
Materials are chosen based on the product’s weight, fragility, and environmental considerations. Common materials include corrugated cardboard for shipping, PET for food-grade packaging, and biodegradable polymers for sustainable solutions.
3. Prototype Fabrication
Fabrication methods depend on the prototype type. Physical prototypes are often created using 3D printing, CNC machining, or die-cutting, while digital prototypes are rendered using virtual simulation tools. Hybrid prototypes may combine both approaches for comprehensive testing.
4. Testing and Iteration
Prototypes undergo rigorous testing to evaluate structural integrity, user experience, and compliance with industry standards. Feedback from stakeholders is incorporated into iterative design improvements, ensuring the final packaging meets all requirements.
What are the Benefits of Packaging Prototypes?
The benefits of packaging prototypes extend beyond design validation, impacting multiple facets of the manufacturing and marketing process.
1. Accelerated Time-to-Market
Prototypes streamline the development process by enabling rapid iterations and early stakeholder feedback, reducing the time required to bring a product to market.
2. Improved Stakeholder Collaboration
Prototypes serve as tangible tools for communication among designers, engineers, marketers, and clients, ensuring alignment and reducing misunderstandings.
3. Competitive Advantage
By refining packaging design and functionality, prototypes help brands differentiate their products in crowded markets, enhancing shelf appeal and consumer engagement.
4. Sustainability
Prototypes enable the exploration of eco-friendly materials and designs, supporting sustainability goals and reducing environmental impact.
What are the Uses of Packaging Prototypes?
Packaging prototypes are utilized across various industries, including food and beverage, cosmetics, electronics, and pharmaceuticals. Their applications include:
- Retail Packaging: Testing visual appeal and shelf presence.
- Shipping and Logistics: Ensuring durability and protection during transit.
- Product Launches: Creating mockups for marketing campaigns and investor presentations.
- Regulatory Testing: Verifying compliance with safety and labeling standards.
Packaging prototypes are indispensable tools for manufacturers, offering a comprehensive approach to design validation, risk mitigation, and market readiness. By integrating advanced fabrication techniques and iterative testing, prototypes ensure that packaging meets functional, aesthetic, and regulatory requirements, ultimately driving product success in competitive markets.