RGB printing is a technique based on the RGB color model, which uses additive color theory to create vibrant and visually appealing prints. Unlike CMYK’s ink-based subtractive method, RGB printing uses light-based color mixing, offering more vivid results but requiring advanced technology. RGB printing is ideal for custom packaging, promotional products, and high-end branding, although challenges like color conversion issues, equipment compatibility, and higher costs persist. Despite these limitations, future trends point toward growing adoption, with innovations like true RGB printers and deeper integration into digital workflows enhancing its potential in luxury and short-run packaging.
What is RGB Printing?
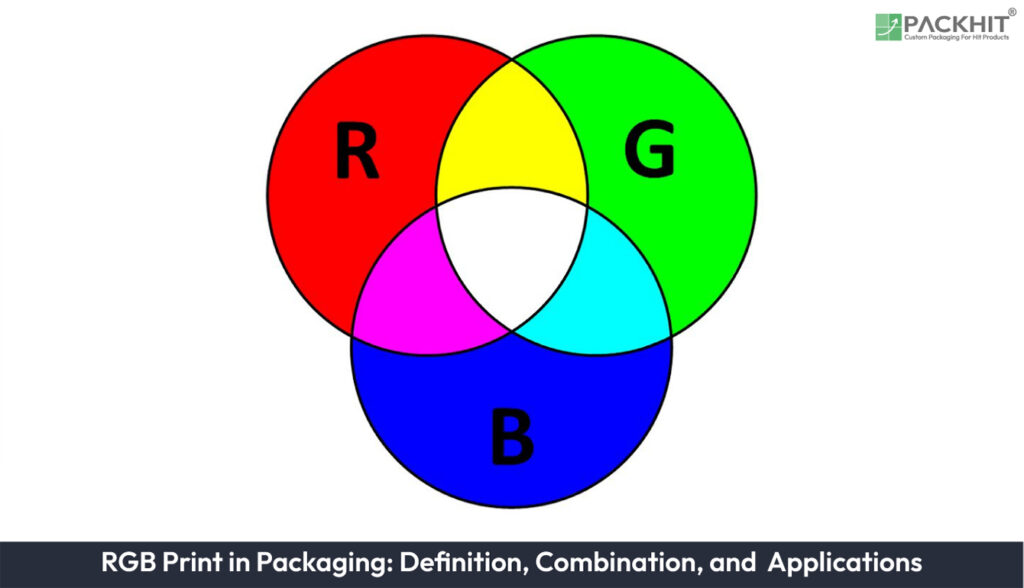
RGB printing refers to a printing technique that utilizes the RGB (Red, Green, Blue) color model. This model is based on additive color mixing, where red, green, and blue light are combined in varying intensities to produce a wide spectrum of colors. Unlike CMYK, which is subtractive and optimized for physical prints, RGB is additive and primarily used for digital displays. However, advancements in printing technology have enabled its application in certain physical printing scenarios, including packaging.
What are the Characteristics of RGB Printing?
RGB printing stands out as a unique approach in the printing industry due to its reliance on the additive color model. Below are the key characteristics that define RGB printing:
- Color Model: RGB (Red, Green, Blue) operates on an additive color model, combining light to produce a wide spectrum of vibrant colors.
- Vivid Color Reproduction: This method is capable of producing highly vibrant, saturated, and visually appealing colors, making it ideal for creating attention-grabbing designs.
- Application in Digital and Specialized Printing: Initially designed for digital displays, RGB printing is now used in specialized packaging applications, particularly where a high level of color vibrancy is desired.
- Color Mixing: RGB printing uses light-based mixing, allowing for more precise and dynamic color combinations compared to traditional ink-based methods.
- Custom Packaging Potential: The ability to produce bold, vivid designs makes RGB printing an excellent choice for custom packaging, promotional products, and high-end branding efforts.
- Technology Dependence: Advanced printing technologies are required to implement RGB color models effectively in physical printing, as most standard printers are designed for CMYK.
These characteristics highlight how RGB printing is particularly suited for applications requiring high-impact visuals, such as limited-edition packaging, promotional items, and luxury branding. However, its use is often limited by technological constraints and higher production costs, necessitating careful consideration for its application.
What is the Difference Between RGB Printing and CMYK Printing?
RGB printing is a technique that uses the additive RGB (Red, Green, Blue) color model, combining light to create vibrant and vivid hues. It is primarily associated with digital displays but is increasingly applied in specialized physical printing scenarios.
CMYK printing, on the other hand, employs a subtractive color model (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Black), mixing inks to produce colors. It is optimized for physical prints and widely used for mass production due to its consistency and compatibility with standard printing equipment.
Below is a detailed comparison of RGB and CMYK printing models, highlighting their key differences and applications:
Key Differences Between RGB and CMYK Printing
| Aspect | RGB Printing | CMYK Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Color Model | RGB (Additive) | CMYK (Subtractive) |
| Color Vibrancy | High | Moderate |
| Applications | Digital displays, specialized packaging | Physical prints, mass production |
| Color Mixing | Light-based | Ink-based |
As demonstrated, RGB printing excels in creating vibrant and vivid hues, making it ideal for digital displays and specialized packaging applications. However, it requires advanced technology for effective physical implementation. In contrast, CMYK printing is optimized for physical prints, offering consistency and compatibility for large-scale production.
Manufacturers should carefully evaluate their specific needs, such as the target medium and desired color output, before choosing between RGB and CMYK printing models. This ensures optimal results in packaging and branding while aligning with technological and budgetary constraints.
What are the Applications of RGB Printing in Packaging?
RGB printing is gaining traction in the packaging industry, particularly for custom and promotional products. Its ability to produce vibrant and visually striking designs makes it a valuable tool for branding and marketing.
Custom Packaging
RGB printing is used to create unique and eye-catching packaging designs that align with a brand’s identity. This is especially beneficial for limited-edition products, promotional campaigns, and high-end merchandise.
Promotional Products
Promotional items such as branded swag, merchandise, and giveaways often utilize RGB printing to achieve vibrant and memorable designs. This enhances brand visibility and customer engagement.
Digital Printing Integration
RGB printing is increasingly integrated into digital printing workflows, allowing manufacturers to experiment with innovative designs and color combinations. This is particularly useful for short-run packaging and prototypes.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its advantages, RGB printing faces certain challenges when applied to physical packaging. These include color mismatches when converting RGB data to CMYK for printing, limited compatibility with traditional printing equipment, and higher costs for specialized applications.
Color Conversion Issues
RGB data must often be converted to CMYK for physical printing, which can result in color discrepancies. This is a common issue for designers who create vibrant RGB designs but face muted results in print.
Equipment Compatibility
Most commercial printers are optimized for CMYK, limiting the direct application of RGB printing. Specialized equipment is required to fully leverage RGB’s capabilities in physical packaging.
Cost Considerations
RGB printing can be more expensive than CMYK due to its specialized nature and the need for advanced equipment. Manufacturers must weigh the benefits against the costs when deciding on its use.
What are the Future Trends in RGB Printing?
The future of RGB printing in packaging looks promising, with advancements in technology enabling wider adoption. Emerging trends include the development of true RGB printers, integration with digital workflows, and increased use in high-end and custom packaging.
True RGB Printers
Innovations such as the LumeJet S200 are paving the way for true RGB printers, which can directly print using the RGB color model without conversion to CMYK. This enhances color accuracy and vibrancy.
Digital Workflow Integration
RGB printing is increasingly being integrated into digital workflows, allowing for seamless transitions between design and production. This is particularly beneficial for short-run and prototype packaging.
High-End Packaging
Luxury brands and high-end products are adopting RGB printing to create visually stunning packaging that stands out in competitive markets. This trend is expected to grow as consumer demand for unique designs increases, offering a unique approach to packaging design and enabling vibrant and visually appealing results.